Tumour Class Prediction using Radiology and Pathology Images Submitted to CPM,MICCAI Devised a workflow for automated interpretation of radiology and pathology images of brain tumours to aid in the detection of tumour subtype. Accomplishment: As a part of computational precision medicine challenge hosted by MICCAI. Model reported an accuracy of 0.75 against the unlabelled dataset. It secured third position in the contest.
COMBINED RADIOLOGY AND PATHOLOGY BASED CLASSIFICATION OF TUMOR TYPES
Computer Aided Detection plays a crucial role in the early detection of deadly diseases such as cancer (or) tumor. Pathology and radiology images form the core of tumor diagnosis. Pathology images provide clinical information about the tissues where as the radiology images can be used for locating the lesions. This work aims at proposing a classification model which categorizes the tumor as oligodendroglioma (benign tumors) (or) astrocytoma (Malignant tumors). The architecture uses dedicated workflows for processing pathology and radiology images.
WORKFLOW FOR TUMOR CLASSIFICATION
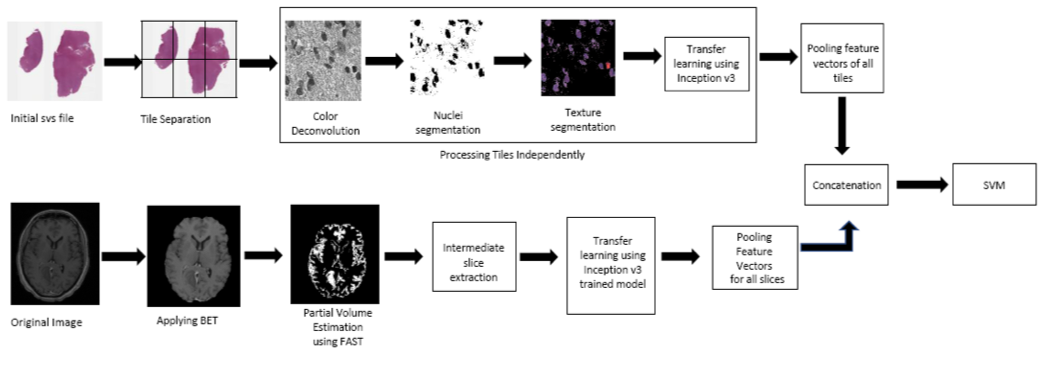
Pathology Image Processing Pipeline:
A whole slide tissue image in SVS format is provided for each case in the dataset. Whole slide images comprises of a pyramid structure holding multiple images at different resolution. VIPS utility is used to tile the baseline image into (256,256) tiles. It’s been recorded in the literature that nuclei appears to have a rough texture in malignant tumors as opposed to smooth regular texture in benign tumors. As the morphology of the nuclei acts as an important attribute in the classification, nuclei is segmented and been used for feature extraction. The pathology images are Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) stained whole slide tissue images. Hematoxylin stain enhances the nuclei in the image. So, Reinhard’s color deconvolution algorithm is applied for the separation of H & E stains from the Image. The H-stained portion of the image is subjected to local maximum clustering for segmentation of nuclei region. The resulting segmentation mask is then applied to the original image for the extraction of the texture details.
Radiology Image Processing Pipeline:
MRI images play a vital role in clinical neuro-imaging in the detection of tumor. They are acquired with several different techniques (pulse sequences) and acquisition parameters (called e.g. echo time, TE, repetition time TR etc.) resulting in different image contrast. The dataset provided all the most common most common MR acquisitions: T1, T1.c, T2 and FLAIR sequences. T1.c MRI is obtained after the administration of contrast media. Tumor regions show signal enhancement after administration of contrast agent and hence T1.c images are considered in the classification task. FSL library is used for analyzing the brain imaging data. The pipeline starts with application of BET command to remove the skull portions . FAST is then applied to categorize the brain regions as grey matter, white matter, CSF and tumor region. The segmented suspicious tissue slices are then fed to Inception V3 and feature vectors are generated independently (i.e) one after the another. med2image package is used in the conversion of Nifti volumes to slices into jpg format. The feature vectors from all the slices are max pooled wherein the maximum of all vectors for each input value is considered. The resulting feature vector is then used for the representation of the radiology image.
Classification model:
The feature vectors from radiology and pathology images are concatenated and are given to the SVM (Support Vector Machine) classification model. SVM is a statistical tool which can learn the non-linear boundaries to separate the data points. As the data points provide a sparse representation, SVM is preferred.